Difference between revisions of "Polyethylene glycol"
m |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | + | {{-}} | |
{| class="toccolours" border="1" style="float: right; clear: right; margin: 0 0 1em 1em; border-collapse: collapse;" | {| class="toccolours" border="1" style="float: right; clear: right; margin: 0 0 1em 1em; border-collapse: collapse;" | ||
! {{chembox header}}| '''{{PAGENAME}}''' <!-- replace if not identical with the article name --> | ! {{chembox header}}| '''{{PAGENAME}}''' <!-- replace if not identical with the article name --> | ||
| Line 32: | Line 32: | ||
|- | |- | ||
|} | |} | ||
| + | |||
'''Polyethylene glycol''' (PEG) and '''polyethylene oxide''' (PEO) are [[polymer]]s having an identical structure except for chain length and end groups, and are the most commercially important [[Ether|polyethers]]. Poly(ethylene glycol) refers to an [[oligomer]] or polymer of ethylene oxide with low [[molecular weight]] while polyethylene oxide is used for higher [[molecular weight]]s. PEG generally is a liquid while PEO is a low-melting solid. Both are prepared by polymerization of [[Ethylene oxide|ethylene oxide]]. While they find use in different applications and have different physical properties (i.e. [[viscosity]]) due to chain length effects, their chemical properties are nearly identical. | '''Polyethylene glycol''' (PEG) and '''polyethylene oxide''' (PEO) are [[polymer]]s having an identical structure except for chain length and end groups, and are the most commercially important [[Ether|polyethers]]. Poly(ethylene glycol) refers to an [[oligomer]] or polymer of ethylene oxide with low [[molecular weight]] while polyethylene oxide is used for higher [[molecular weight]]s. PEG generally is a liquid while PEO is a low-melting solid. Both are prepared by polymerization of [[Ethylene oxide|ethylene oxide]]. While they find use in different applications and have different physical properties (i.e. [[viscosity]]) due to chain length effects, their chemical properties are nearly identical. | ||
Latest revision as of 22:48, 11 September 2009
| Template:Chembox header| Polyethylene glycol | |
|---|---|
| |
| Chemical name | Polyethylene glycol |
| Chemical formula | CxHxNxOx |
| Molecular mass | xx.xx g/mol |
| CAS number | [xx-xx-xx] |
| Density | x.xxx g/cm3 |
| Melting point | xx.x °C |
| Boiling point | xx.x °C |
| SMILES | xxxx |
| Template:Chembox header | Disclaimer and references | |
Polyethylene glycol (PEG) and polyethylene oxide (PEO) are polymers having an identical structure except for chain length and end groups, and are the most commercially important polyethers. Poly(ethylene glycol) refers to an oligomer or polymer of ethylene oxide with low molecular weight while polyethylene oxide is used for higher molecular weights. PEG generally is a liquid while PEO is a low-melting solid. Both are prepared by polymerization of ethylene oxide. While they find use in different applications and have different physical properties (i.e. viscosity) due to chain length effects, their chemical properties are nearly identical.
Its melting point is around 68 degree Celsius.
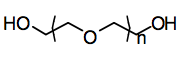
Polyethylene glycol has the following structure:
- HO-(CH2-CH2-O)n-H
PEGylation is the act of covalently coupling a PEG structure to another larger molecule, for example, a therapeutic protein (which is then referred to as PEGylated). PEGylated interferon alfa-2a or -2b is a commonly used injectable treatment for Hepatitis C infection.
PEG is soluble in water, methanol, benzene, dichloromethane and is insoluble in diethyl ether and hexane. It is coupled to hydrophobic molecules to produce non-ionic surfactants.
Clinical uses
Polyethylene glycol is non-toxic and is used in a variety of products. It is the basis of a number of laxatives (e.g. macrogol-containing products such as Movicol® and polyethylene glycol 3350, or MiraLax®). It is the basis of many skin creams, as cetomacrogol, and sexual lubricants, frequently combined with glycerin. Polyethylene glycol with added electrolytes is used for bowel preparation and drug overdoses. It is sold under the brand names GoLYTELY and Colyte. When attached to various protein medications, polyethylene glycol allows a slow clearance of the carried protein from the blood. This makes for a longer acting medicinal effect and reduces toxicity, and it allows longer dosing intervals. Examples include PEG-interferon alpha which is used to treat hepatitis C and PEG-filgrastim (Neulasta®) which is used to treat neutropenia. It has been shown that polyethylene glycol can improve healing of spinal injuries in dogs [1]. One of the earlier findings that polyethylene glycol can aid in nerve repair came from the University of Texas (Krause and Bittner) [2]. Polyethylene glycol is commonly used to fuse B-cells with myeloma cells in monoclonal antibody production.
Other uses
PEG is used in a number of toothpastes as a dispersant; it binds water and helps keep gum uniform throughout the toothpaste. It is also used in liquid body armor [3] and tattoos to monitor diabetes[4]. Functional groups of PEG give polyurethane elastomers their "rubberiness", for applications such as foams (foam rubber) and fibers (spandex). Its backbone structure is analogous to that of silicone, another elastomer.
Since PEG is a flexible polymer, it can be used to create very high osmotic pressures (tens of atmospheres). It also is unlikely to have specific interactions with biological chemicals. These properties make PEG one of the most useful molecules for applying osmotic pressure in biochemistry experiments, particularly when using the osmotic stress technique. [5]
PEO (polyethylene oxide) can serve as the separator and electrolyte solvent in lithium polymer cells. Its low diffusivity often requires high temperatures of operation, but its high viscosity even near its melting point allows very thin electrolyte layers. While crystallization of the polymer can degrade performance, many of the salts used to carry charge can also serve as a kinetic barrier to the formation of crystals. Such batteries carry greater energy for their weight than other lithium ion battery technologies.
Polyethylene glycol is also commonly used as a polar stationary phase for gas chromatography, as well as a heat transfer fluid in electronic testers.
PEG is included in many or all formulations of the soft drink Dr Pepper, purportedly as an anti-foaming agent.